Load Balancer Definition
A load balancer manages the flow of information between the server and an endpoint device (PC, laptop, tablet or smartphone). A load balancer is a hardware or software solution that helps to move packets efficiently across multiple servers, optimizes the use of network resources and prevents network overloads.
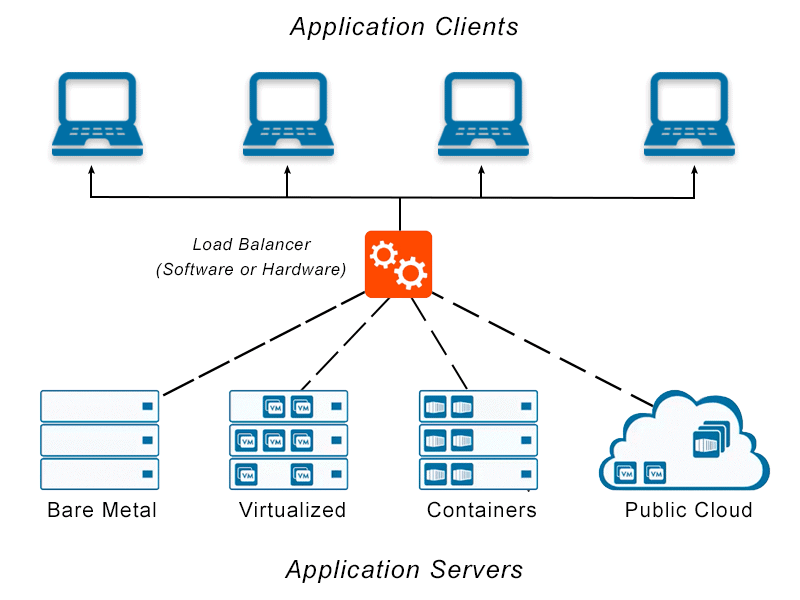
How Does A Load Balancer Work?
As an organization meets demand for its applications, the load balancer plays the role of the traffic cop in the network, deciding which servers can handle that traffic. This traffic management is intended to deliver a good user experience. Load balancers monitor the health of web servers and backend servers to ensure they can handle requests. If necessary, it removes unhealthy servers from the pool until they are restored. Some even trigger the creation of new virtualized application servers to cope with increased demand and maintain response times. The most effective load balancers operate with workloads across multiple environments (on-premises and cloud) and diverse infrastructures (bare metal servers, VMs, and containers).
Software Load Balancer Vs Hardware Load Balancer
The types of load balancers may include hardware, virtual, or software. Traditionally, load balancers consist of a hardware or virtual appliance. Increasingly, and in order to meet the needs of modern applications, they are using software-defined architectures. Hardware load balancers are optimized to run on custom processors. As traffic increases, the vendor simply requires the addition of more load balancer appliances to handle the volume. Software load balancers usually run on less-expensive, standard x86 hardware, virtual machines, or event containers. These are also particularly well-suited in cloud environments like Amazon AWS or Microsoft Azure where physical appliances cannot be deployed.
Why Use A Software Load Balancer?
Using a software load balancer provides the following benefits:
- Flexibility to adjust for changing needs.
- Ability to scale beyond initial capacity by adding more software instances.
- Lower cost than purchasing and maintaining proprietary hardware appliances. Software can run on any standard hardware or virtual machine, which tends to be cheaper.
- Consistent load balancing capabilities across multiple cloud environments.
Why Use A Load Balancer In Cloud Computing?
Using a cloud load balancer provides a managed application networking solution in the cloud that can draw resources from a network of elastic load balancers and servers. Cloud computing also allows for the flexibility of hybrid, hosted, and multi-cloud solutions. They could be deployed on-premises as well as in the cloud and managed centrally.
The Network Load Balancer and Application Services
Load balancers occupy an important position in the path of application traffic on a network. Yet, traditional application delivery controllers (ADCs) are unable to provide meaningful application insights to drive business decisions. As computing moves to the cloud, virtual ADCs perform similar tasks to hardware. They also come with added functionality and flexibility. Today’s software load balancers do more than ensure high availability. They let an organization quickly and securely scale up its application services based on demand in the cloud. Modern ADCs allow organizations to consolidate network-based services. Those services include SSL/TLS offload, caching, compression, intrusion detection and application firewalls. This creates even shorter delivery times and greater scalability.
Does VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer Offer A Load Balancer?
Yes. The VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer’s Intent-based Software Load Balancer provides scalable application delivery across any infrastructure. VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer provides 100% software load balancing to ensure a fast, scalable and secure application experience. It delivers elasticity and intelligence across any environments. It scales from 0 to 1 million SSL transactions per second in minutes. It achieves 90% faster provisioning and 50% lower TCO than traditional appliance-based approach.
For more on the actual implementation of load balancers, check out our Application Delivery How-To Videos.
For more information on multi-cloud see the following resources: