Infrastructure as a Service Definition
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) hosts infrastructure on the public cloud and private cloud instead of in a traditional on-premises data center. The infrastructure is delivered to customers on demand while being fully managed by the service provider.
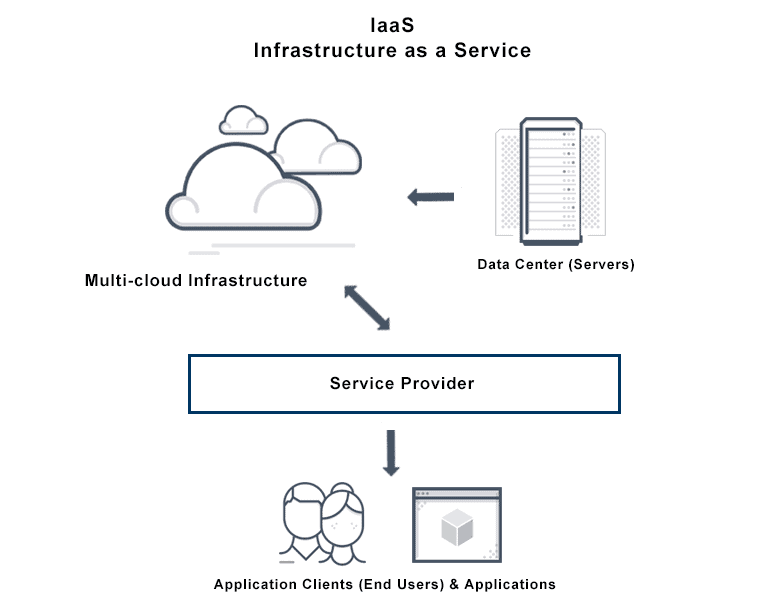
What is Infrastructure as a Service?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing service where enterprises rent or lease servers for compute and storage in the cloud. Users can run any operating system or applications on the rented servers without the maintenance and operating costs of those servers. Other advantages of Infrastructure as a Service include giving customers access to servers in geographic locations close to their end users. IaaS automatically scales, both up and down, depending on demand and provides guaranteed service-level agreement (SLA) both in terms of uptime and performance. It eliminates the need to manually provision and manage physical servers in data centers.
What are the Benefits of Infrastructure-as-a-Service?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) can be more efficient for an enterprise than owning and managing its own infrastructure. New applications can be tested with an IaaS provider instead of acquiring the infrastructure for the test.
Other advantages of infrastructure-as-a-service include:
- Continuity and disaster recover – Cloud service in different locations allows access to applications and data during a disaster or outage.
- Faster scaling – Quickly scale up and down resources according to application demand in all categories of cloud computing.
- Core focus – IaaS allows enterprises to focus more on core business activities instead of IT infrastructure and computing resources.
How to Implement Infrastructure as a Service?
The implementation can be in a public, private or hybrid cloud setting. Customers use a graphical interface to change the infrastructure as needed. The infrastructure can also be accessed through an API key — so new servers are brought online as part of an automation when needed.
Enterprises use IaaS to do the following more efficiently:
- Test and development – Test and development environments are fast and easy to set up with IaaS. This allows for bringing applications to market quicker.
- Backup and recover – IaaS solves for storage management and recovery issues. It handles unpredictable demand and storage needs without the enterprise having to dedicate staff to manage it.
- Big data analysis – IaaS provides the processing power to economically mine large data sets.
How Does Infrastructure as a Service Work?
IaaS started in the cloud as one of the service layers including Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS). Customers use dashboards and APIs to directly access their servers and storage. With IaaS, there is higher scalability.
IaaS users enjoy many advantages of Infrastructure as a service, such as accessing the same infrastructure technology services of a traditional data center without having to invest as many resources. It is a flexible cloud computing model that allows for automated deployment of servers, processing power, storage and networking.
Does the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer Work With Infrastructure as a Service?
Yes. Many companies that use IaaS to host their applications can also use the VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer to deliver the applications. The VMware NSX Advanced Load Balancer SaaS is the cloud-hosted option to deliver application services including distributed load balancing, web application firewall, global server load balancing (GSLB), network and application performance management across a multi-cloud environment. It helps ensure fast time-to-value, operational simplicity, and deployment flexibility in a highly secure manner.
For more on the actual implementation of load balancing, security applications and web application firewalls check out our Application Delivery How-To Videos.
For more information see the following Infrastructure-as-a-Service resources: